Loop Control Statements in Python
In addition to common control statements like if-else, while loops, and for loops, Python includes special loop control statements that offer more control over program execution. These are:
- break
- continue
- pass
Each of these statements has unique features that allow you to control the flow of your program in ways that standard control statements may not.
1. Python break
The break statement is used to exit a loop prematurely, stopping the loop’s execution entirely. This can be useful when you need to terminate the loop based on a specific condition.
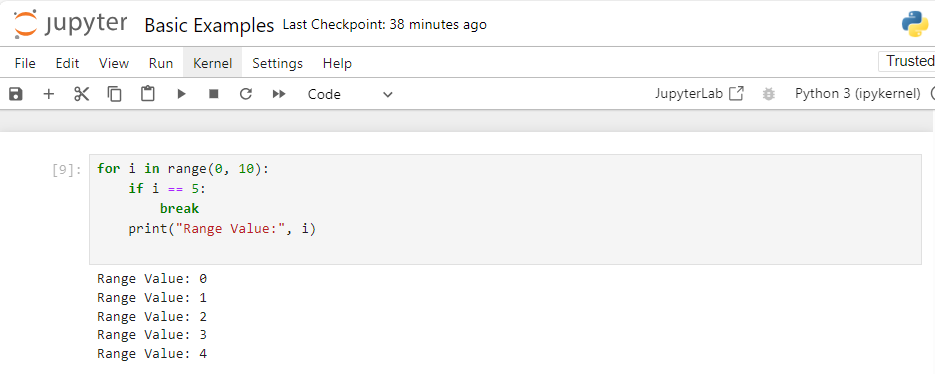
Example 1: Breaking a For Loop
for i in range(0, 10):
if i == 5:
break
print("Range Value:", i)
In this example, the loop stops running when i equals 5, and no further values are printed.
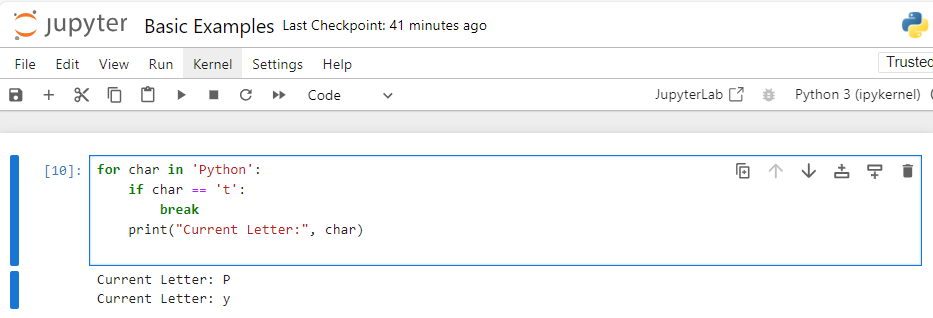
Example 2: Breaking a Loop in a String
for char in 'Python':
if char == 't':
break
print("Current Letter:", char)
Here, the loop exits when it encounters the letter ‘t‘, so only the letters before ‘t’ are printed.
These examples illustrate how the break statement allows you to exit loops early based on specific conditions, enhancing your control over the flow of your program.
2. CONTINUE
The continue statement skips the rest of the code in the current iteration and moves to the next iteration of the loop.
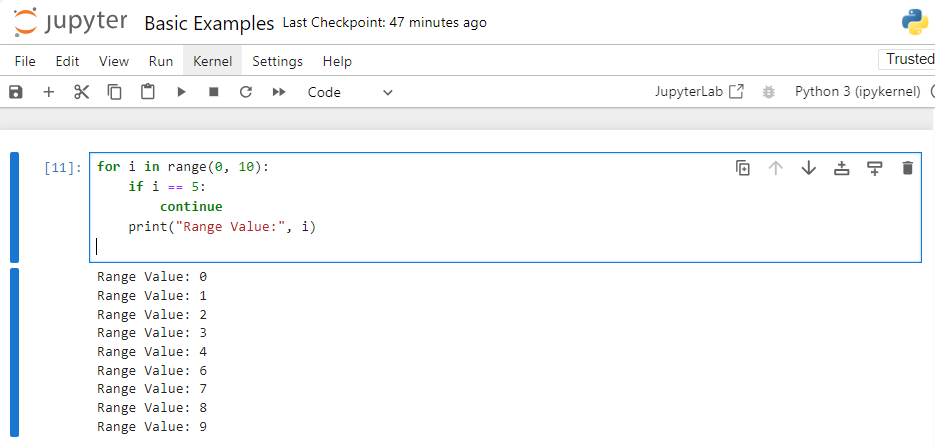
Example 1: Using Continue in a For Loop
for i in range(0, 10):
if i == 5:
continue
print("Range Value:", i)
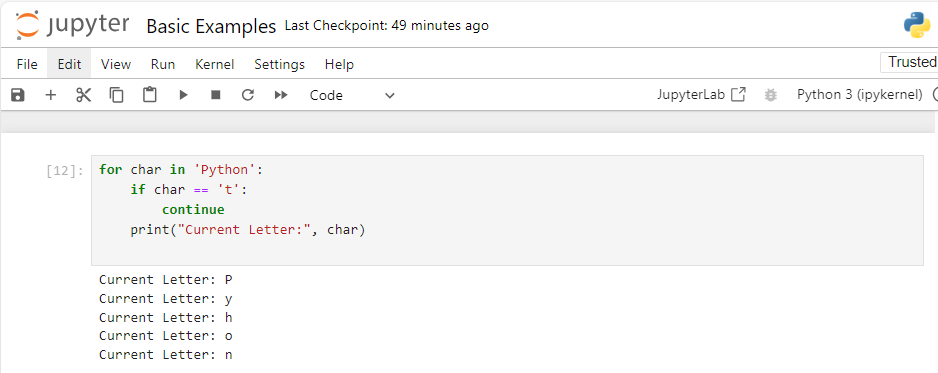
Example 2: Using Continue with a String
for char in 'Python':
if char == 't':
continue
print("Current Letter:", char)
3. PASS
The pass statement is a placeholder that does nothing when executed. It is useful during development when you want to leave a block of code empty but still need to maintain the structure of your program.
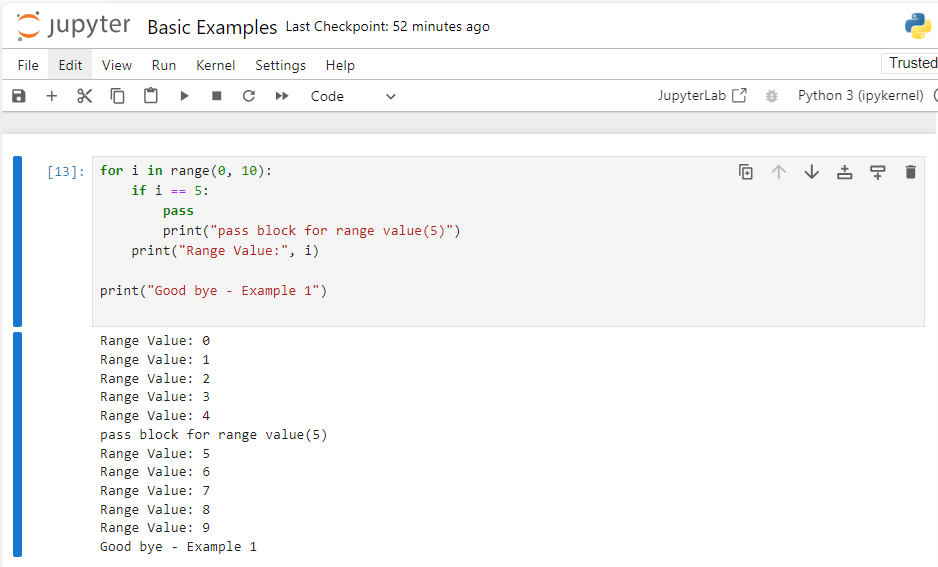
Example 1: Using Pass in a For Loop
for i in range(0, 10):
if i == 5:
pass
print("pass block for range value(5)")
print("Range Value:", i)
print("Good bye - Example 1")
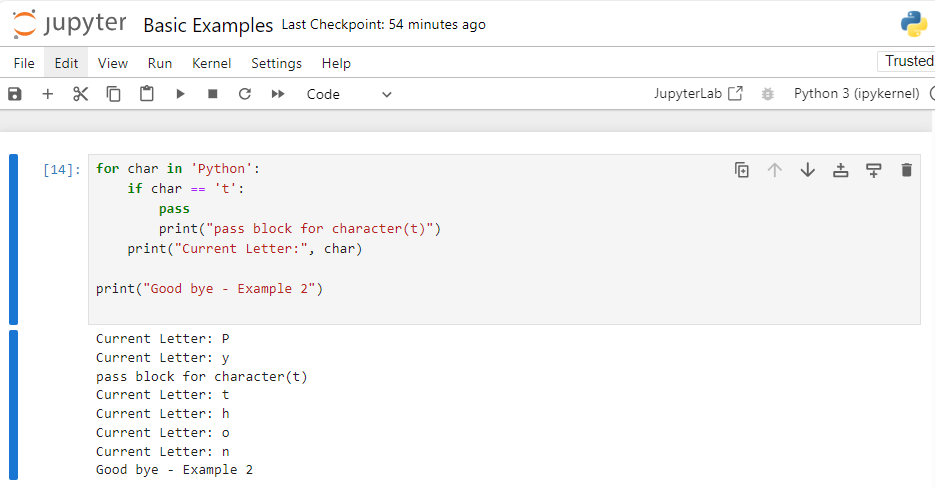
Example 2: Using Pass with a String
for char in 'Python':
if char == 't':
pass
print("pass block for character(t)")
print("Current Letter:", char)
print("Good bye - Example 2")
Summary
Python offers special loop control statements—python break, continue, and pass—to manage the flow of loops more effectively:
- Break: Exits a loop completely when a specific condition is met.
- Continue: Skips the current iteration and moves to the next one.
- Pass: Acts as a placeholder, doing nothing when executed, useful during development.
These statements give you greater flexibility in controlling program execution within loops.
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES:
- How to define and call functions in Python?
- Control statements in Python: break, continue, pass keywords
- If-Else Statement in Python
- For loop and While loop in Python
- Python IDLE, Shell and Command Prompt (Guide)
- Exception handling in Python
- Python Variables, data types, and values
- Python function arguments
- Python interactive mode and script mode programming
- How To Install and Download Python Anaconda?
- Python Raise Keyword
- What is Python? Why it is most loved programming language?
- Write your first Python program!
- Zen of Python and Anti-Zen of Python
- Best Python books to read and learn!